Are you feeling a bit powerless when it comes to understanding AC vs. DC power? Don’t worry, you’re not alone! It’s a shocking topic that can leave even the brightest sparks feeling a bit dim. But fear not, we’re here to shed some light on the electrifying differences between these two currents. So sit back, relax, and get ready to plug in to the world of AC vs. DC power explained in a way that’s sure to spark your interest! Let’s amp up your knowledge and switch on to the differences between these electrifying power sources.
Overview of AC and DC Power
When it comes to power, there are two main players in the game – AC and DC. Think of them as the Batman and Superman of electricity. Both have their own strengths and weaknesses, but ultimately they work together to keep our world powered up.
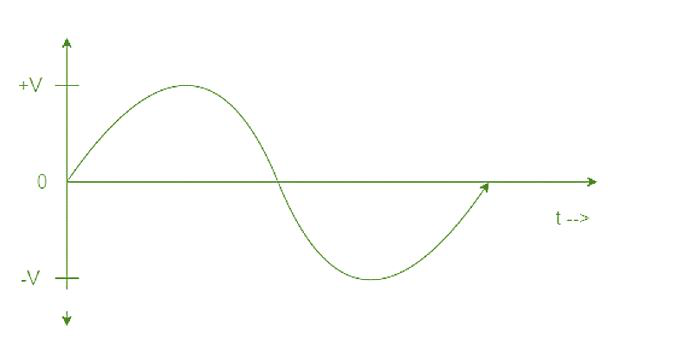
AC, also known as alternating current, is like the life of the party. It’s constantly changing direction, switching back and forth like a game of musical chairs. This lively current is what powers our homes, offices, and just about everything else that needs electricity.
On the other hand, DC, or direct current, is more like the quiet genius in the corner. It flows in one continuous direction, steady and reliable. DC is what you’ll find in batteries, cars, and other electronics that need a consistent power source.
So, next time you flip a switch or charge your phone, remember that we owe it all to the dynamic duo of AC and DC. They may have their differences, but when it comes down to it, they’re the power couple that keeps the lights on and the world spinning.
Key Characteristics of Alternating Current (AC)
AC, the cool cousin of DC, is known for its unique characteristics that set it apart in the world of electrical currents. Here are some key characteristics that make AC stand out:
- **Bidirectional flow:** AC has the amazing ability to change directions constantly, never sticking to just one path like its boring cousin, DC. It’s like that friend who’s always switching up plans at the last minute, keeping you on your toes.
- **Voltage fluctuations:** AC loves to keep you guessing with its constantly changing voltage levels. It’s like trying to predict the weather in a tropical storm – one minute it’s calm, the next it’s a wild dance party of electrons.
- **Easy transmission:** AC travels long distances with ease, thanks to its ability to transform into different voltage levels. It’s like that friend who can adapt to any situation, whether it’s a fancy dinner party or a wild night out.
- **Efficient power distribution:** AC is the life of the electrical grid party, effortlessly flowing through power lines and delivering energy to homes and businesses. It’s like the Energizer Bunny of electricity, powering through obstacles with unstoppable energy.
Key Characteristics of Direct Current (DC)
DC, also known as direct current, has a few key characteristics that make it stand out from its flashy cousin AC – Alternating Current. So, what makes DC so special? Well, let me break it down for you in true electrifying fashion.
First off, DC flows in one direction like a smooth operator gliding through a dance floor. There’s no back and forth like a ping pong match – it’s just a straight shot from point A to point B. Talk about efficiency! Plus, DC is like the strong, silent type – it gets the job done without any unnecessary drama.
Another key characteristic of DC is its stability. It’s like that reliable friend who always shows up on time and never lets you down. With DC, you don’t have to worry about any sudden spikes or drops in voltage – it’s a steady Eddie all the way.
And let’s not forget about the simplicity of DC. It’s as straightforward as a straight line – no complicated waveforms or frequency changes to deal with. Just good old-fashioned current flowing in a single direction. It’s like the basic, no-frills option on a menu full of flashy AC dishes. Just plug in and go, no fuss, no muss.
In conclusion, DC may not be the life of the party like AC, but it’s definitely the reliable, steady-Eddie you want in your corner when things get electric. So next time you’re in need of some current with a bit of swagger, remember the key characteristics of DC – smooth, stable, and simple. Who says electricity can’t have a sense of humor
Applications of AC Power
AC power, also known as alternating current, is a versatile form of electrical power that has a wide range of applications in our everyday lives. From powering our homes to running industrial machinery, AC power keeps the world moving and grooving!
One of the most common uses of AC power is in household appliances such as refrigerators, air conditioners, and washing machines. These appliances rely on AC power to function properly and make our lives easier (and cooler!). Can you imagine trying to keep your food cold with DC power? It would be a melting disaster!
AC power is also essential in the world of entertainment and technology. Everything from TVs to computers to sound systems relies on AC power to bring the magic to life. Without AC power, our movie nights would be silent and our Netflix binges would be non-existent. Thank goodness for AC power!
Industrial are also crucial for keeping factories and manufacturing plants running smoothly. Heavy machinery, assembly lines, and conveyor belts all require the power of AC to keep churning out products at lightning speed. Without AC power, these industrial wonders would grind to a halt faster than a sloth on a treadmill!

Applications of DC Power
In a world where DC power reigns supreme, the applications are endless! From powering your favorite gadgets to keeping the lights on in your home, DC power is truly versatile. Let’s explore some fun and quirky ways DC power can be utilized:
- Charging your smartphone: Say goodbye to low battery anxiety with the help of DC power. Just plug in your charger, sit back, and watch as your phone regains its energy.
- Powering electric cars: Who needs gasoline when you can cruise around town in a sleek electric vehicle powered by good ol’ DC power? Not only will you be saving the planet, but you’ll also be turning heads with your eco-friendly ride.
- Operating solar panels: Harness the power of the sun with the help of DC power. By converting sunlight into electricity, you can reduce your carbon footprint and lower your energy bills – all while basking in the glow of renewable energy.
So, the next time you flip a switch or charge your device, remember the power of DC power! It may not be as flashy as its AC counterpart, but it sure knows how to get the job done with style and efficiency. Embrace the electrifying world of DC power – you won’t be disappointed!
Advantages and Disadvantages of AC Power
Some advantages of AC power include:
- Versatility: AC power can be easily transformed into different voltages, making it suitable for a variety of devices.
- Efficiency: AC power is more efficient for long-distance power transmission compared to DC power.
- Cost-Effective: AC power distribution systems are generally less expensive to install and maintain.
However, there are also some disadvantages to AC power:
- Power Loss: AC power can suffer from power loss due to factors such as resistance and inductance.
- Electromagnetic Interference: AC power can generate electromagnetic interference, which can affect sensitive electronic devices.
- Safety Hazards: AC power can be more dangerous than DC power, especially in terms of electrical shock risks.
Advantages and Disadvantages of DC Power
There are definitely pros and cons when it comes to using DC power. Let’s break it down, shall we?
Advantages:
- No energy loss in transmission
- Great for smaller electronics
- Simple to transform voltage levels
- More cost-effective for shorter distances
Disadvantages:
- Not practical for long-distance transmission
- Requires specialized equipment for conversion
- Can be dangerous if not handled correctly
- Not as common as AC power
So, there you have it! DC power may have its perks, but it also comes with its fair share of drawbacks. It all depends on what you need it for and how you plan to use it. Choose wisely!
FAQs
Q: Can you charge my phone with AC power?
Sure, you can charge your phone with AC power! Just plug your phone charger into a wall outlet and you’re good to go.
Q: Can I use DC power to run my toaster?
Sorry, but your toaster needs AC power to run. DC power won’t be able to give your bread that crispy goodness.
Q: What’s the deal with AC and DC power anyway?
AC power is like that cool friend who switches things up all the time – it flows back and forth in a wave-like motion. DC power, on the other hand, is more like that reliable friend who always keeps it steady - it flows in one direction only.
Q: Which type of power is better for long-distance transmission?
AC power takes the crown for long-distance transmission because it can be easily stepped up or down using transformers. DC power, on the other hand, would be like trying to run a marathon in flip-flops – not the most efficient option.
Q: Can I convert AC power to DC power?
Absolutely! You can use a device called a rectifier to convert AC power to DC power. It’s like magic, but with electricity!
—
In Summary:
And there you have it, folks! The shocking truth about AC vs. DC power. Hopefully, this article has shed some light on the electrifying differences between the two. Remember, when it comes to powering up your devices, it’s all about alternating current for versatility or direct current for reliability. So next time you plug something in, just think: are you feeling wild and unpredictable like AC, or steady and constant like DC? The choice is in your hands (literally)! Stay powered up, and may the current be ever in your favor! ⚡🔌