In the fantastical world of biology, where creatures great and small frolic in the jungle of evolutionary relationships, two mighty warriors stand tall: the Cladogram and the Phylogenetic Tree. These two cunning diagrams wield their branches and nodes as weapons in the eternal battle for classification supremacy. Join us as we embark on a thrilling quest through the tangled vines of organism relationships, where alliances are forged, enemies are vanquished, and evolution reigns supreme. Let the battle of the diagrams begin!
Overview of Evolutionary Relationships
Evolutionary relationships are basically like a big family tree, except instead of Aunt Sally and Uncle Bob, you’ve got species and genera branching off from each other like crazy. It’s like trying to figure out who is related to who at a family reunion after a few too many glasses of Aunt Linda’s famous spiked punch.
Scientists use a variety of tools to piece together these evolutionary relationships, from studying fossils to analyzing DNA sequences. It’s like playing a game of genetic Clue – ”Was it Mr. T. Rex in the Mesozoic era with the sharp teeth, or Mrs. Homo sapiens in the Pleistocene with the opposable thumbs?”
Through these investigations, researchers can determine which species are distant cousins, which are long-lost siblings, and which are just straight-up strangers in the evolutionary world. It’s like the ultimate episode of Who Do You Think You Are?, but with a lot more prehistoric drama and a lot less Lisa Kudrow.
So next time you look at a phylogenetic tree and see a bunch of crazy branches and connections, just remember that it’s all part of the big, beautiful evolutionary family tree. And who knows, maybe you and that cockroach crawling around your kitchen are more closely related than you think. Talk about awkward family reunions!

Defining Cladograms and Phylogenetic Trees
What’s the deal with cladograms and phylogenetic trees? Well, let me break it down for you in the most entertaining way possible. Imagine a family tree on steroids – that’s essentially what a cladogram is. It’s a way to visually represent evolutionary relationships between different species. Think of it as a roadmap tracing back the origins of all living creatures, from unicellular organisms to complex mammals.
Now, phylogenetic trees take this concept to a whole new level. They’re like the ultimate family reunion, showing how all living organisms are interconnected through a complex web of evolutionary history. It’s like playing a game of genetic Six Degrees of Kevin Bacon, except instead of actors, you’re linking species based on shared evolutionary traits.
In a cladogram, species are grouped together based on shared characteristics, with each branch representing a common ancestor. It’s like a high school clique, where certain species are deemed cool enough to hang out together in the same group. And just like in high school, there’s always that one species that doesn’t quite fit in with the rest - poor little evolutionary outcast.
So next time you look at a cladogram or phylogenetic tree, remember that it’s not just a boring diagram. It’s a visual representation of the epic saga of evolution, complete with its own cast of characters and plot twists. Who knew science could be so entertaining
Comparing and Contrasting Cladograms and Phylogenetic Trees
Ever find yourself getting confused between cladograms and phylogenetic trees? Don’t worry, you’re not alone! While they may seem similar at first glance, there are some key differences that set them apart. Let’s break it down for you:
Cladograms are like the flashy, trendy cousin at the family reunion – they focus on showing evolutionary relationships through branching patterns. Think of them as a family tree on steroids, with each branch representing a common ancestor. Phylogenetic trees, on the other hand, are more traditional and reserved. They show the evolutionary history of a group of organisms in a more linear fashion, emphasizing the sequence of speciation events.
One way to think about it is that cladograms are like a modern art piece – abstract and open to interpretation. Phylogenetic trees, on the other hand, are like a classic oil painting – detailed and precise. Both are beautiful in their own way, but it really comes down to personal preference.
So, next time you’re trying to make sense of the tangled web of evolutionary relationships, remember the difference between cladograms and phylogenetic trees. Whether you’re a fan of the flashy or the traditional, both tools are essential for understanding the complex world of biodiversity. Just don’t mix them up at your next biology exam!

Analyzing the Utility of Cladograms in Phylogenetics
Do cladograms really hold all the secrets to understanding the evolutionary relationships between organisms, or are they just fancy tree diagrams that make scientists feel smart? Let’s dig deep into the utility of cladograms in phylogenetics and see if they truly live up to the hype.
First off, cladograms sure do look cool with their branching patterns and fancy labels. It’s like a family tree on steroids, making even the most boring of organisms seem interesting. Plus, they make you feel like a legit scientist when you’re presenting your research – who wouldn’t want that ego boost?
But when it comes down to the nitty-gritty of actually using cladograms to decipher evolutionary relationships, things can get a little messy. Sure, they can help us visualize how different species are related to each other, but interpreting all those squiggly lines and nodes can give anyone a headache. It’s like trying to solve a Rubik’s cube while blindfolded – fun at first, but ultimately frustrating.
Despite their quirks and complexities, cladograms do serve an important purpose in phylogenetics. They provide a framework for organizing and comparing the vast diversity of life on Earth, helping us unravel the mysteries of evolution one branch at a time. So next time you’re knee-deep in cladogram chaos, just remember – it’s all part of the scientific adventure!
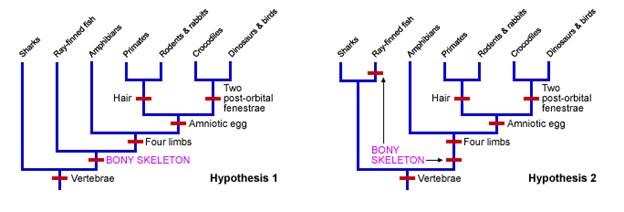
Examining the Complexities of Building Phylogenetic Trees
When it comes to building phylogenetic trees, things can get a bit… complicated. Like trying to untangle a ball of yarn with one hand tied behind your back. But fear not, brave scientist! We’re here to guide you through the maze of evolutionary relationships with a few laughs along the way.
First off, let’s talk about the sheer number of species out there. It’s like trying to find Waldo in a sea of look-alikes. With millions of different organisms to compare, it’s no wonder that building a phylogenetic tree can feel like searching for a needle in a haystack. But hey, at least you’ll become an expert at spotting the difference between a frog and a toad.
Now, let’s not forget about all the different methods for building phylogenetic trees. It’s like having a buffet of options, but without any labels to tell you what’s what. From distance-based algorithms to maximum parsimony, it’s enough to make your head spin faster than a tornado. Just remember, when in doubt, trust the data… and maybe flip a coin for good measure.
And let’s not even get started on the debate between molecular and morphological data. It’s like trying to decide between cake and ice cream – why not both? But beware, mixing the two can lead to more confusion than a chameleon at a rainbow convention. So, choose wisely and may the phylogenetic gods be ever in your favor.
Interpreting Evolutionary History Through Cladistics
Have you ever wondered how scientists interpret evolutionary history through a method called cladistics? Well, prepare to have your mind blown as we delve into the world of phylogenetic trees, shared derived traits, and nested hierarchies!
Picture this: you’re a dinosaur enthusiast trying to figure out how all those prehistoric monsters are related to each other. With cladistics, scientists can group these creatures based on shared characteristics known as synapomorphies. This is basically like creating a family tree – the T-Rex is Uncle Bob, the Stegosaurus is Cousin Sally, and the Velociraptor is that weird second cousin twice removed.
Cladistics uses a fancy method called parsimony to figure out the most likely evolutionary relationships. It’s like playing a game of “Guess Who?” except instead of eliminating characters with mustaches, you’re eliminating traits like feathers or scales. Oh, the drama!
So next time you see a phylogenetic tree, remember that each branch represents a common ancestor, and each node represents a speciation event. It’s basically a family reunion where some branches are the well-behaved cousins, while others are the black sheep of the family – looking at you, pterodactyls!
Future Directions in Understanding Organism Relationships
As we venture into uncharted territory in understanding organism relationships, the possibilities are as vast as a heaping pile of elephant dung. One exciting frontier is the study of symbiotic relationships, where organisms live together in harmony, kind of like a quirky roommate situation. Whether it’s parasitic worms hitching a ride on a host or algae providing nutrients for coral reefs, these partnerships make Tinder look like child’s play.
Another direction for exploration is the fascinating world of predator-prey relationships. It’s like a high-stakes game of hide and seek, with one organism trying to outsmart the other for survival. Picture a lion stalking a zebra or a Venus flytrap luring its unsuspecting prey with promises of a gourmet meal. It’s nature’s own version of reality TV, complete with drama, suspense, and occasional bloodshed.
But wait, there’s more! With advancements in genetic sequencing, we can now delve deeper into the microscopic world of microbial relationships. Bacteria swapping genes like trading cards, fungi forming alliances with plant roots, viruses hijacking host cells for their own nefarious purposes – the possibilities are as endless as a buffet line at a cockroach convention. Who knew that the tiniest of organisms could have the juiciest gossip?
So buckle up, fellow travelers of the scientific realm, because the future of understanding organism relationships is as unpredictable as a chameleon at a rainbow convention. With each new discovery, we get one step closer to unraveling the intricacies of the interconnected web of life. Who knows what bizarre, mind-boggling relationships await us just around the corner? It’s a wild, wacky world out there – let’s dive in headfirst and see where the journey takes us!
FAQs
What’s the difference between a cladogram and a phylogenetic tree?
Cladograms are like the hipster version of phylogenetic trees - they show relationships based solely on shared derived characteristics, while phylogenetic trees are the classic, all-inclusive family tree of life.
Which one is more accurate in representing organism relationships?
Well, that’s like asking if a Monet painting is more accurate than a Bob Ross landscape. Cladograms give a more focused snapshot of evolutionary relationships, while phylogenetic trees aim to show the big picture. Both have their strengths and weaknesses.
Can you use both cladograms and phylogenetic trees together?
Absolutely! Think of it like getting a genetic test and digging through your family tree on Ancestry.com. Combining both methods can give you a more comprehensive understanding of how organisms are related.
Are there any famous examples of using cladograms or phylogenetic trees in scientific research?
Oh, definitely! It’s like the Kardashians of the scientific world – everyone’s talking about them. Scientists have used cladograms and phylogenetic trees to trace the evolutionary history of everything from dinosaurs to bacteria.
How do scientists decide which organisms to include in a cladogram or phylogenetic tree?
It’s like picking squads for dodgeball - they choose organisms that are closely related or have unique characteristics that can shed light on evolutionary relationships. It’s all about finding the right mix to create a balanced and informative tree.
Can regular folks like us understand and appreciate cladograms and phylogenetic trees?
Of course! It’s like learning to appreciate fine wine or artisanal cheese – it just takes a little time and effort. Once you dive into the world of organism relationships, you’ll start seeing the beauty and complexity of life’s family tree.
—
Time to Branch Out
Phew! Who knew learning about organism relationships could be so tree-mendously fun? Whether you prefer the sleek lines of a cladogram or the twisty branches of a phylogenetic tree, one thing’s for sure – we’re all just trying to make sense of this crazy tree of life. So go forth, explore, and may your knowledge of organism relationships continue to grow like a well-tended tree. Happy branching!






