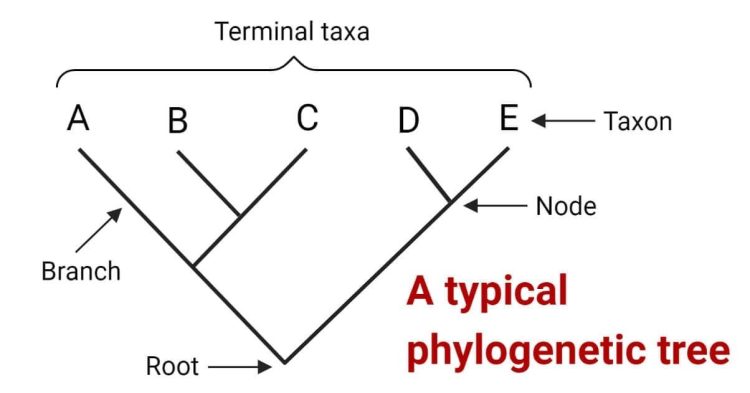
In the tangled forest of scientific classification, evolutionary trees stand tall as the arboreal architects of the natural world. These majestic cladograms, with limbs reaching back through time, are the blueprint for understanding the interconnected branches of life. Join us as we uncover the secrets of constructing these intricate family trees and discover the evolutionary stories they whisper from leaf to root. So grab your binoculars and let’s explore the wild world of cladistics with a dash of humor and a sprinkle of scientific sass!
Overview of Evolutionary Trees
So you want to learn about Evolutionary Trees, huh? Well, buckle up because we’re about to dive deep into the wacky world of how all living things are related!
Evolutionary trees are basically like the family trees you see on Ancestry.com, except instead of tracing your lineage back to some long-lost relative who was a knight or a queen (sorry to burst your bubble), we’re tracing the history of life on Earth back billions of years. It’s like one big, twisted game of Six Degrees of Separation, except instead of Kevin Bacon, we’re all related to single-cell organisms and dinosaurs.
These trees show the relationships between different species based on their shared evolutionary history. Think of it like a big game of connect-the-dots, where each dot represents a different species and the lines connecting them show how they evolved from a common ancestor. It’s like some kind of crazy family reunion where everyone’s arguing over who inherited Aunt Mildred’s antique vase.
And just like any good family tree, these Evolutionary Trees can get pretty complicated. With branches branching off branches and stems splitting into twigs, it’s enough to make your head spin faster than a squirrel on a spinning wheel. But fear not! We’re here to guide you through the chaos and show you just how beautifully intertwined the web of life really is. So grab your binoculars and get ready to explore the wild world of Evolutionary Trees!

Understanding Cladistics and Phylogenetics
Cladistics is like playing a game of “guess who” with organisms. Scientists look at their traits and lineage to figure out who’s related to who in the family tree of life. It’s like creating a big, messy family reunion seating chart where Uncle Bob gets seated next to his distant cousin twice removed.
Phylogenetics takes this family tree and turns it into a scientific detective novel. It’s all about unraveling the mystery of evolutionary relationships between different species. Think Sherlock Holmes, but instead of a magnifying glass, we use DNA sequences and morphological characteristics to piece together the puzzle of who evolved from who.
Imagine a Venn diagram on steroids, with overlapping circles representing shared characteristics between organisms. Cladistics and phylogenetics help us make sense of this tangled web of relationships and create a roadmap of evolutionary history. It’s like drawing a giant family tree of life, complete with branches, leaves, and the occasional black sheep.

Importance of Morphological and Molecular Data
When it comes to understanding the evolutionary history of organisms, both morphological and molecular data play a crucial role. These two types of data complement each other like peanut butter and jelly – they’re great on their own, but together they create a delightful sandwich of knowledge!
Let’s start with morphological data – the OG method of studying organisms. From the shape of a leaf to the size of a tooth, morphological data gives us valuable clues about the relationships between different species. It’s like comparing puzzle pieces to see how they fit together in the big picture of evolution.
On the other hand, molecular data takes us down to the nitty-gritty of genetics. By examining DNA sequences, we can uncover hidden connections between species that may not be obvious from their outward appearance. It’s like looking at the blueprint of life itself to unravel the mysteries of evolution.
So, next time you’re puzzling over the family tree of a group of organisms, remember to gather both morphological and molecular data. With these tools in hand, you’ll be equipped to uncover the secrets of evolution and unlock the mysteries of the natural world!

Principles of Constructing Cladograms
Constructing cladograms is a lot like solving a complex puzzle – except this puzzle involves evolutionary relationships and molecular data instead of finding the missing piece of a jigsaw. Here are some principles to keep in mind when constructing cladograms that will help you navigate through the craziness of phylogenetics:
- **Homoplasy is the enemy**: Homoplasy is that annoying friend who copies your outfit and makes it difficult to distinguish between shared ancestry and convergent evolution. Be vigilant in recognizing homoplasy and avoid including it in your cladogram like a bad outfit choice.
- **Keep it simple, stupid**: Remember the KISS principle when constructing your cladogram – you’re not trying to impress anyone with unnecessary complexity. Stick to the simplest explanation that fits the data, just like how simplicity is key when ordering a fast-food meal.
- **Outgroup love**: Don’t forget about your outgroup – they may not be as cool or trendy as the ingroup, but they provide invaluable information for rooting your cladogram. Give your outgroup some love and appreciation, even if they’re the awkward third wheel in your evolutionary analysis.
Techniques and Software for Phylogenetic Analysis
Whether you’re a seasoned geneticist or a beginner bioinformatician, diving into the world of phylogenetic analysis can be both exciting and overwhelming. Luckily, there are a plethora of techniques and software available to help you navigate this complex field with ease.
From traditional methods like Maximum Likelihood and Bayesian inference to cutting-edge algorithms like Neighbor Joining and UPGMA, there’s no shortage of tools at your disposal. And let’s not forget about the software – programs like MEGA, MrBayes, and BEAST are here to make your life a whole lot easier.
But wait, there’s more! Want to visualize your phylogenetic trees in style? Look no further than FigTree and iTOL. Need to annotate your sequences? SeaView and BioEdit have got you covered. With so many options available, you’ll be a phylogenetic pro in no time.
So grab your lab coat, fire up your computer, and get ready to unravel the mysteries of evolution with these top-notch techniques and software. Who knew that analyzing DNA sequences could be this fun?
Challenges and Limitations of Evolutionary Tree Construction
Evolutionary tree construction can be a tricky business, with many challenges and limitations to navigate. One major issue is the massive amount of data that needs to be analyzed. It’s like trying to untangle a giant ball of yarn while blindfolded – except instead of yarn, it’s DNA sequences.
Another challenge is the fact that evolution doesn’t always follow a straight line. It’s more like a choose-your-own-adventure story, with twists and turns at every corner. Just when you think you’ve got it figured out, a new piece of evidence comes along and sends you back to the drawing board.
And let’s not forget about the limitations of the tools themselves. Sometimes it feels like trying to build a house with only a hammer and a roll of duct tape. Sure, you can make it work, but it’s not going to be pretty.
Despite these challenges and limitations, evolutionary tree construction continues to be a vital tool in understanding the history of life on Earth. So, next time you’re feeling overwhelmed by the complexities of phylogenetics, just remember – at least you’re not trying to untangle that giant ball of yarn.
FAQs
Why do scientists use cladograms to study evolutionary relationships?
Well, my friend, trying to figure out who’s related to who in the vast tree of life is no easy task! Cladograms are like the ultimate family tree for all living things. They help scientists track the evolutionary history of organisms and see how they’re all connected.
How do scientists actually construct these complex diagrams?
Oh, it’s a whole process, let me tell you! Scientists gather all sorts of data on different traits and characteristics of organisms – from physical features to genetic code. Then, they analyze and compare all this information to see who’s got what in common. It’s like playing a big game of biological connect-the-dots!
What’s the deal with all those fancy branching lines on a cladogram?
Those lines are like the highways of evolution, showing how different species have branched off from common ancestors over time. Each branch represents a “clade,” a group of organisms that share a common ancestor. So basically, it’s like a family reunion for all living things!
Can cladograms ever change or be updated?
Absolutely! Evolution is a wild and unpredictable ride, so cladograms are always subject to change as new evidence comes to light. Just like rearranging your family tree after finding out you’re actually related to that distant aunt twice removed - science is always evolving!
Do cladograms have any practical applications outside of science?
Oh, you bet! Understanding evolutionary relationships can help us in all sorts of ways, from developing new medicines based on shared genetic traits to conserving endangered species by identifying their closest relatives. So the next time you pop a pill or visit a zoo, just thank those trusty cladograms for guiding the way!
—
And remember…
Evolutionary trees may make you feel like you’re lost in a dense forest of scientific jargon, but fear not! With a little patience, a dash of curiosity, and maybe a good pair of binoculars, you too can navigate the wild world of cladograms. So go forth, dear reader, and let the branches of knowledge guide you on your evolutionary journey!