Are you feeling charged up to learn about the electrifying world of ionic and molecular compounds? Get ready to dive deep into the chemical abyss as we compare these two contrasting compounds in an electrifying showdown. From shocking revelations to molecular mysteries, this in-depth analysis will have you buzzing with excitement. So grab your lab coat and safety goggles, because things are about to get seriously science-y in here! Let the battle of the compounds commence!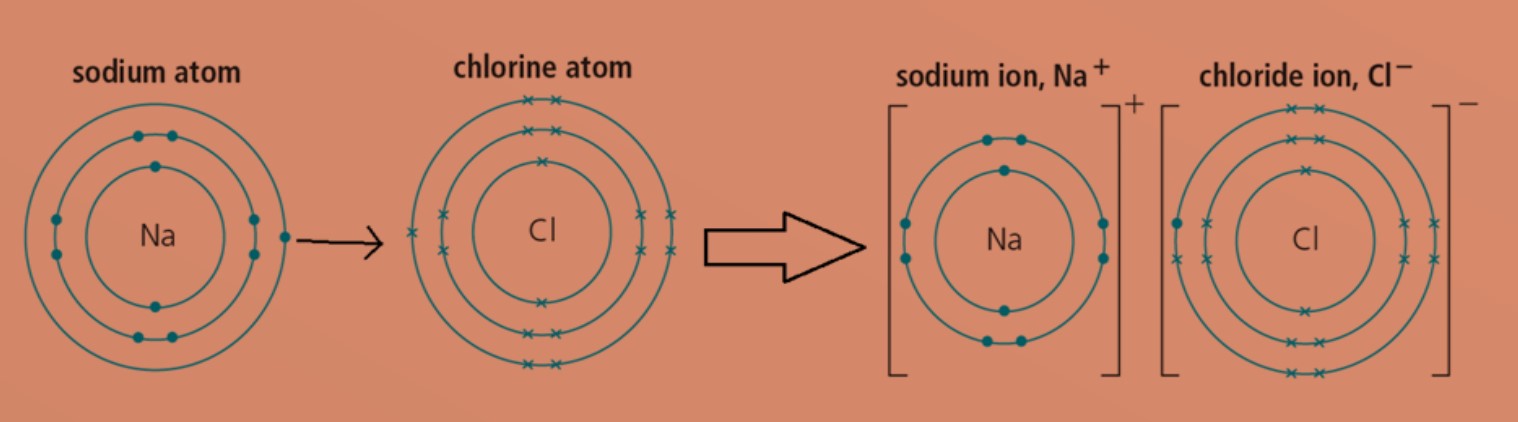
Key Differences Between Ionic and Molecular Compounds
So, you’re in chemistry class and you’re trying to wrap your head around the differences between ionic and molecular compounds. Don’t worry, I’ve got you covered with the key distinctions that will help you ace that next exam!
First off, let’s talk about the bonding in these compounds. Ionic compounds form when atoms transfer electrons, creating ions that are attracted to each other due to their opposite charges. On the other hand, molecular compounds are made up of covalently bonded atoms that share electrons. Think of ionic compounds as the dramatic rom-com couples who are constantly pulling each other in with their magnetic attraction, while molecular compounds are more like the laid-back friends who are happy to share everything.
Next up, let’s discuss their physical properties. Ionic compounds tend to have high melting and boiling points because of the strong electrostatic forces between ions. Molecular compounds, on the other hand, have lower melting and boiling points because the intermolecular forces between molecules aren’t as strong. It’s like the difference between trying to separate two magnets glued together versus two friends holding hands – one requires a lot more force!
And finally, let’s talk about their solubility. Ionic compounds are often soluble in water because the polar water molecules can easily surround and dissolve the charged ions. On the flip side, molecular compounds may or may not be soluble in water, depending on their polarity. It’s like trying to fit square pegs into round holes – some compounds just don’t mix well with others!

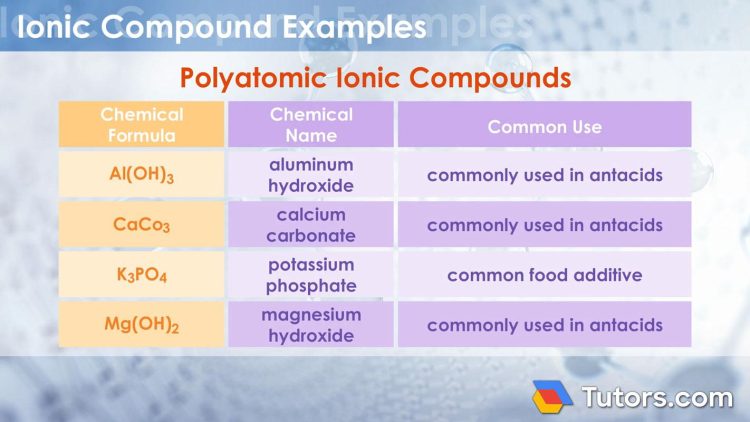
Ionic Compounds: Formation and Properties
When it comes to ionic compounds, things can get a little charged! These compounds are formed through the transfer of electrons between atoms, resulting in the formation of positively and negatively charged ions. This transfer creates strong electrostatic forces that hold the ions together, creating the infamous crystal lattice structure that gives ionic compounds their unique properties.
One of the most fascinating aspects of ionic compounds is their ability to conduct electricity when dissolved in water or melted. This is due to the movement of the ions, which carry an electric charge, allowing them to flow freely and conduct electricity. It’s like a tiny, invisible dance party happening right before our eyes!
Another interesting property of ionic compounds is their high melting and boiling points. This is because of the strong electrostatic forces between the positively and negatively charged ions, which require a lot of energy to overcome. So next time you’re cooking up a storm in the kitchen, just remember that those salt crystals are holding on tight!
Overall, ionic compounds are a fascinating and electrifying group of substances that play a crucial role in our everyday lives. From table salt to ceramics, these compounds are all around us, creating the perfect balance of positive and negative energy. So next time you come across an ionic compound, give it a little salute for all the electrifying properties it brings to the table!
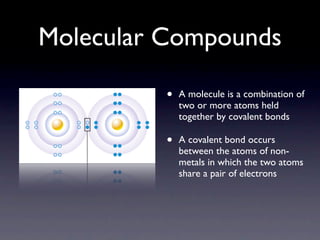
Molecular Compounds: Formation and Properties
Molecular compounds are like the ultimate power couple in the chemistry world. They come together in perfect harmony to form these amazing structures that have unique properties that make them stand out from the crowd.
One of the coolest things about molecular compounds is how they are formed. It’s like a chemical love story – atoms from different elements join forces through covalent bonds to create these amazing molecules. They share electrons like it’s the hottest gossip in town, forming strong bonds that hold them together in their molecular union.
When it comes to properties, molecular compounds are just as unique as the individuals that make them up. They can be solid, liquid, or gas at room temperature, depending on their structure and composition. Some are sweet as sugar, while others can be as volatile as a bad breakup. But no matter what, they all have their own quirks that make them special.
So next time you see a molecular compound, remember that it’s not just a random collection of atoms – it’s a masterpiece of chemical creativity that has its own set of rules and quirks. And who knows, maybe you’ll find your own chemistry love story in the world of molecular compounds.
Comparing Physical Properties of Ionic and Molecular Compounds
When it comes to comparing the physical properties of ionic and molecular compounds, there are some key differences that set them apart. Let’s break it down in a fun and lighthearted way!
One major difference between ionic and molecular compounds is their melting and boiling points. Ionic compounds typically have higher melting and boiling points compared to molecular compounds. This is because the strong electrostatic forces between ions in an ionic compound require more energy to break apart, while molecular compounds have weaker intermolecular forces that can be easily overcome.
Another notable difference is their solubility in water. Ionic compounds, due to their charged ions, are usually soluble in water because they can easily interact with the polar water molecules. On the other hand, molecular compounds may or may not be soluble in water depending on their polarity. It’s like trying to fit a square peg into a round hole – some compounds just don’t mix well!
Lastly, the conductivity of ionic and molecular compounds also sets them apart. Ionic compounds are typically good conductors of electricity when dissolved in water or in a molten state, as their charged ions can move freely to carry an electric current. In contrast, molecular compounds do not conduct electricity well because their molecules do not have any charged particles to facilitate the flow of electricity. It’s like trying to power up a light bulb with a potato – it’s not going to work!

Chemical Reactions of Ionic and Molecular Compounds
Let’s dive into the fascinating world of chemical reactions involving both ionic and molecular compounds. It’s like a chemical dance party – with atoms!
First up, we have ionic compounds. These bad boys love to give away or steal electrons to achieve stability. When an ionic compound reacts, it’s like watching a high-stakes game of electron hot potato. One minute an atom has an extra electron, the next - bam! It’s given it away to its buddy. Who knew chemistry could be so dramatic?
On the other hand, molecular compounds are a bit more chill. They prefer to share electrons, forming strong covalent bonds. It’s like a chemistry version of roommates sharing a pizza – everyone gets a fair share! When molecular compounds react, they cozy up and swap atoms like trading cards at recess. It’s all about finding that perfect balance.
So there you have it, the wacky world of chemical reactions with ionic and molecular compounds. Whether it’s ions playing electron tag or molecules sharing their atoms, chemistry sure knows how to keep us on our toes! Who knew science could be so entertaining?
Real-World Applications of Ionic and Molecular Compounds
Ever wonder how everyday items like table salt and baking soda are made? Well, wonder no more! Ionic and molecular compounds are the unsung heroes behind these common household products.
One real-world application of ionic compounds is in the production of fireworks. That’s right, those beautiful bursts of color in the sky are made possible by the careful combination of different metal salts. Each metal salt emits a specific color when ignited, creating a dazzling display for all to enjoy.
On the molecular side of things, consider the sweet satisfaction of biting into a piece of chocolate. Molecular compounds like sucrose give chocolate its irresistible taste. And let’s not forget about caffeine – another molecular compound found in coffee that gives us the energy boost we need to conquer the day.
So, next time you reach for the salt shaker or sip on a cup of coffee, remember the vital role that ionic and molecular compounds play in our daily lives. From fireworks to chocolate, these compounds are truly everywhere, quietly working their magic behind the scenes.
FAQs
What are the defining characteristics of an ionic compound?
Well, an ionic compound is like that one friend who always steals your snacks – it’s all about the transfer of electrons. You’ve got positively charged cations and negatively charged anions just hanging out together, forming a crystal lattice structure.
And what about molecular compounds?
Oh, these are like the cool kids in chemistry class who form covalent bonds by sharing electrons. They don’t need to steal snacks because they’re already a tight-knit group, sharing everything from electrons to bad chemistry jokes.
How do the physical properties of ionic and molecular compounds differ?
Think of ionic compounds as the jocks – they have higher melting and boiling points, and are usually solid at room temperature. Meanwhile, molecular compounds are more like the artsy band kids – lower melting and boiling points, and they can be solid, liquid, or gas at room temperature depending on who they’re vibing with.
Can you give an example of each type of compound?
Oh sure! Take sodium chloride for ionic - it’s table salt, that stuff you sprinkle on your fries and popcorn. For molecular, think of water – H2O. You know, that essential compound for life that also doubles as a surprisingly fun way to cool off on a hot day.
How do you predict the formula of an ionic compound?
It’s like playing chemistry matchmaker - you’ve got to balance the charges to make sure everyone’s happy. The charges on the cation and anion have to cancel out, just like in a successful blind date. Love is in the air!
Are there any exceptions to the rules when comparing ionic and molecular compounds?
Of course, because what’s chemistry without a little drama? There are molecular compounds with high melting and boiling points, and there are even ionic compounds that break the rules and exist as liquids at room temperature. It’s like chemistry’s way of keeping you on your toes.
—
The Battle of the Compounds: Ionic vs Molecular
And there you have it, folks! The epic showdown between ionic and molecular compounds has finally come to an end. So who emerged victorious in this fierce competition? Well, the truth is, both compounds have their own unique strengths and weaknesses, much like rival superheroes in a comic book.
Whether you’re Team Ionic or Team Molecular, one thing is for sure – both types of compounds play a crucial role in our everyday lives. So let’s raise a toast to these unsung heroes of the chemical world and continue to marvel at the wonders of chemistry. Until next time, stay bonded and keep those electrons spinning!